Many people believe that thicker insulation boards are better for cold storage, but this is actually a misconception. The key to selection lies in comprehensive consideration, rather than simply pursuing thickness.
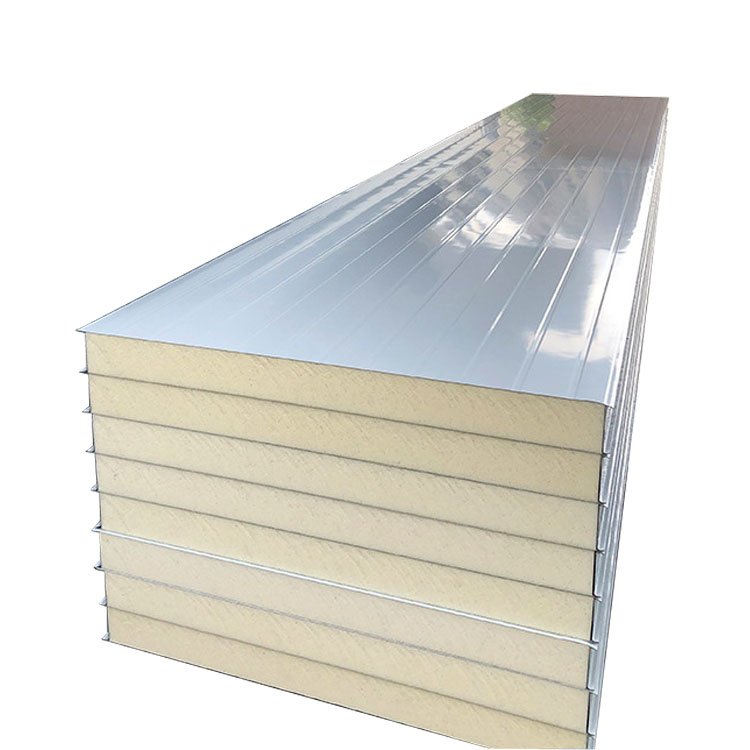

Polyurethane (PU): with the best performance and low thermal conductivity, it is the preferred choice for medium and low temperature cold storage.
Polystyrene (EPS): Poor thermal insulation, but inexpensive, commonly used in cold storage with low temperature requirements.
A high-quality PU board with a thickness of 100mm may have a much better insulation effect than a 150mm thick EPS board.
0 ℃~+10 ℃ (fresh storage): commonly used 100mm~120mm thick.
-18 ℃~-25 ℃ (freezer): commonly used 150mm-200mm thick.
-Below 30 ℃ (ultra-low temperature storage): 200mm or more is required.
Thin boards can cause air conditioning leaks and skyrocket electricity bills; Thick boards will waste construction space and costs.
First, let's look at the materials: prioritize high-performance materials such as polyurethane (PU).
On demand selection: Determine the appropriate thickness based on actual temperature requirements.
General ledger: Although good insulation requires a slightly higher initial investment, it is more energy-efficient and cost-effective in the long run.
Ultimately, the selection of cold storage panels is a precise trade-off between material performance, thickness, space utilization, and overall cost of ownership. Seeking advice from a professional cold chain design company before project initiation is the most reliable way to ensure efficient, energy-saving, and long-term stable operation of cold storage.

Material is more important than thickness
The core of insulation performance is the thermal conductivity of the material, and the lower the value, the better the insulation.Polyurethane (PU): with the best performance and low thermal conductivity, it is the preferred choice for medium and low temperature cold storage.
Polystyrene (EPS): Poor thermal insulation, but inexpensive, commonly used in cold storage with low temperature requirements.
A high-quality PU board with a thickness of 100mm may have a much better insulation effect than a 150mm thick EPS board.
The thickness needs to match the temperature
The thickness should be scientifically selected based on the design temperature of the cold storage:0 ℃~+10 ℃ (fresh storage): commonly used 100mm~120mm thick.
-18 ℃~-25 ℃ (freezer): commonly used 150mm-200mm thick.
-Below 30 ℃ (ultra-low temperature storage): 200mm or more is required.
Thin boards can cause air conditioning leaks and skyrocket electricity bills; Thick boards will waste construction space and costs.
Conclusion:
Choosing a cold storage panel is not about the thicker the better, but about:First, let's look at the materials: prioritize high-performance materials such as polyurethane (PU).
On demand selection: Determine the appropriate thickness based on actual temperature requirements.
General ledger: Although good insulation requires a slightly higher initial investment, it is more energy-efficient and cost-effective in the long run.
Ultimately, the selection of cold storage panels is a precise trade-off between material performance, thickness, space utilization, and overall cost of ownership. Seeking advice from a professional cold chain design company before project initiation is the most reliable way to ensure efficient, energy-saving, and long-term stable operation of cold storage.