As temperatures continue to rise, cold storage equipment is facing enormous pressure due to the surge in cooling demand. Overloading operation may lead to equipment failure, soaring energy consumption, and even safety accidents. To ensure stable operation of cold storage in high temperature environments, the following are five key protective measures.
Prevent overheating: Regularly maintain the motor and refrigeration pipeline to avoid burning or refrigerant leakage caused by high temperature.
Balanced load: If there are multiple refrigeration units, allocate refrigeration tasks reasonably to avoid single machine overload.
Strengthen insulation measures: Check the sealing strip of the warehouse door and the insulation layer of the wall to reduce air leakage.
Optimize temperature control settings: While ensuring storage safety, adjust the temperature settings appropriately to reduce frequent compressor starts and stops.
Add auxiliary cooling equipment: such as exhaust fan or spray cooling system to reduce the ambient temperature of the unit.
Reduce direct sunlight: Use reflective coatings or sunshades on the exterior walls of the cold storage to reduce the impact of thermal radiation.
Voltage stabilizing device: prevents equipment from being damaged by voltage fluctuations during peak electricity consumption periods.
Temperature alarm system: Set up automatic alarm for abnormal temperature rise, intervene in a timely manner to avoid cargo damage.
Emergency shutdown process: Develop standardized response procedures for unexpected situations such as overheating and overpressure.
Spare parts reserve: Prepare vulnerable parts such as fuses, relays, and refrigerants in advance to shorten maintenance time.

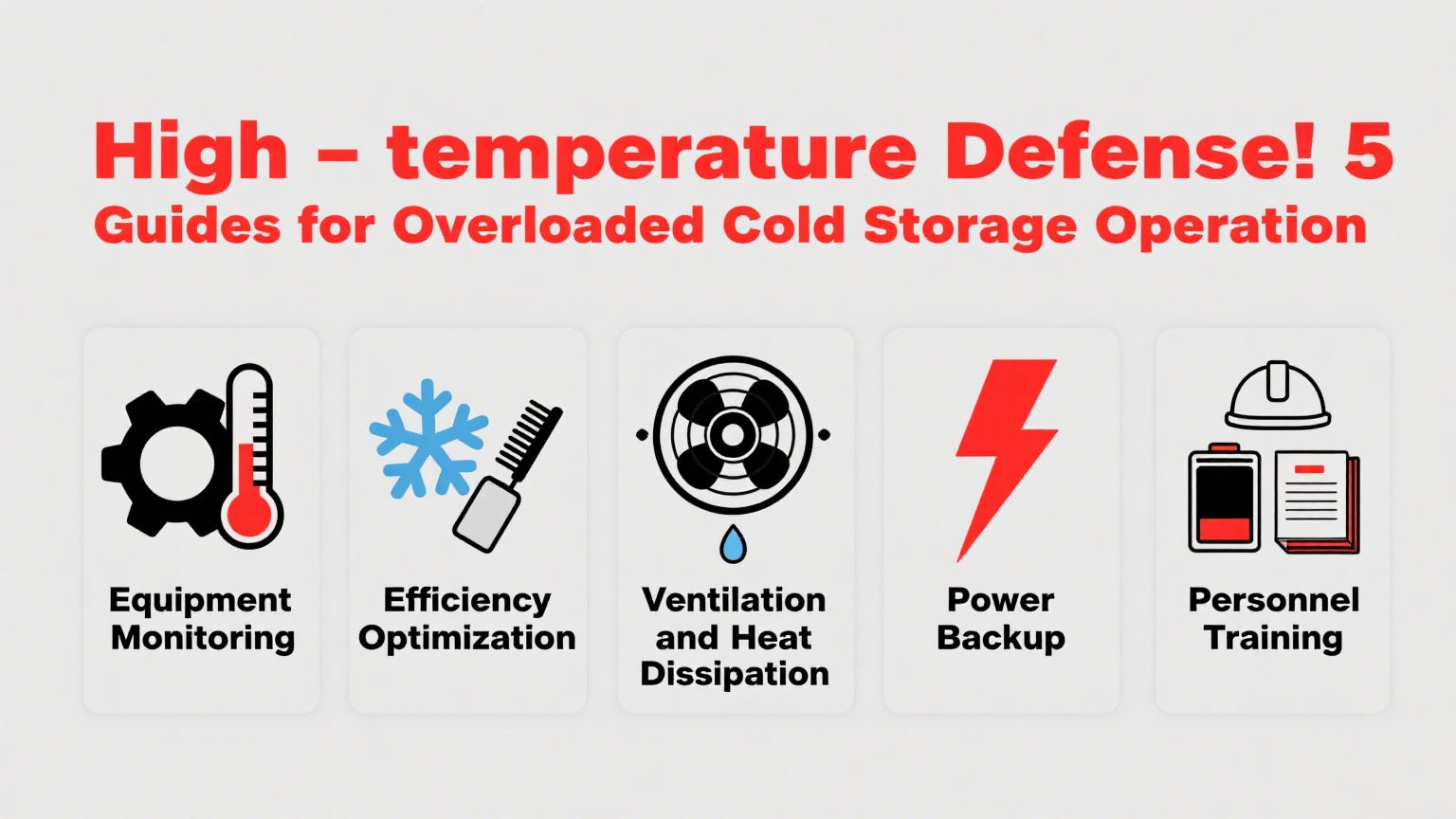
Equipment monitoring and load management
Real time monitoring: Install temperature and current sensors to track the operating status of compressors, condensers, and evaporators in real time.Prevent overheating: Regularly maintain the motor and refrigeration pipeline to avoid burning or refrigerant leakage caused by high temperature.
Balanced load: If there are multiple refrigeration units, allocate refrigeration tasks reasonably to avoid single machine overload.
Improve refrigeration efficiency
Cleaning the condenser and heat sink: Dust accumulation at high temperatures can seriously affect heat dissipation, and cleaning frequency needs to be increased.Strengthen insulation measures: Check the sealing strip of the warehouse door and the insulation layer of the wall to reduce air leakage.
Optimize temperature control settings: While ensuring storage safety, adjust the temperature settings appropriately to reduce frequent compressor starts and stops.
Strengthen ventilation and heat dissipation
Ensure equipment ventilation: Install the condenser in a cool and ventilated area to avoid high temperature environments exacerbating the load.Add auxiliary cooling equipment: such as exhaust fan or spray cooling system to reduce the ambient temperature of the unit.
Reduce direct sunlight: Use reflective coatings or sunshades on the exterior walls of the cold storage to reduce the impact of thermal radiation.
Emergency power supply guarantee
Backup generator: to deal with the problem of frequent power outages in summer.Voltage stabilizing device: prevents equipment from being damaged by voltage fluctuations during peak electricity consumption periods.
Temperature alarm system: Set up automatic alarm for abnormal temperature rise, intervene in a timely manner to avoid cargo damage.
Personnel training and emergency response plan
Employee training: Identify equipment abnormalities (such as abnormal noise, excessive frost) and master basic disposal methods.Emergency shutdown process: Develop standardized response procedures for unexpected situations such as overheating and overpressure.
Spare parts reserve: Prepare vulnerable parts such as fuses, relays, and refrigerants in advance to shorten maintenance time.