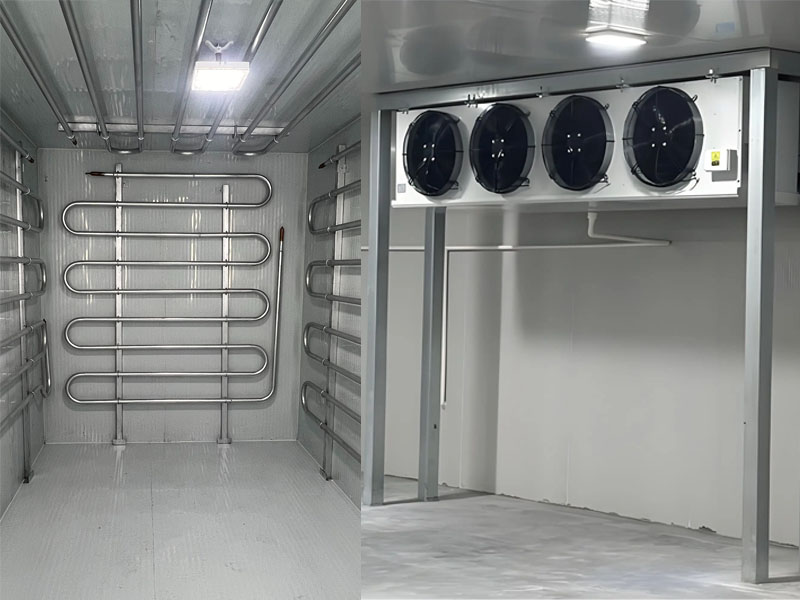
In industrial refrigeration and commercial cold storage systems, the selection of evaporators is often the key to determining system efficiency and energy consumption. Among them, air coolers and coil evaporators are the two most commonly used evaporator solutions. With rising energy costs and heightened environmental awareness, choosing more energy-efficient and high-performance options has become a focal point for enterprises. This article will provide an in-depth comparison of these two technologies to help you make more informed decisions in your projects.

Gravity Coil: The natural convection cooling rate is slow, but the temperature fluctuation is small, suitable for long-term storage and environments with high humidity requirements.
Gravity Coil: No fan consumes power, the system runs quietly, but in high temperature environments, the compressor load may increase due to low heat exchange efficiency.
Gravity Coil: Natural convection is not easy to take away moisture, and the humidity inside the warehouse is well maintained, making it suitable for fresh-keeping storage.
Frequent inbound and outbound distribution centers
Places with high requirements for cooling speed
Scenarios with limited space requiring compact design
A fresh-keeping warehouse with high humidity requirements
Cold storage with long storage time and low frequency of inbound and outbound operations
Environment sensitive to noise
Gravity Coil: requires a large amount of copper or aluminum pipes, with high material and installation costs.
Gravity Coil: No moving parts, low failure rate, but long defrosting cycle and difficult pipeline cleaning.
Gravity Coil: The lifespan of the pipeline system can be over 15 years, with low maintenance requirements.
Gravity Coil: Optimize pipeline layout and materials (such as aluminum pipes) to improve heat transfer efficiency and reduce filling volume.
Usage mode (temperature, turnover frequency of goods, number of door openings)
Energy prices
Initial budget and long-term operating costs
Food preservation requirements
For low-temperature storage facilities located in areas with long-term frozen storage and high electricity prices, the long-term energy-saving benefits of pipeline drainage are more significant.
During the design and selection phase, conduct a full lifecycle cost analysis (including initial investment, electricity consumption, maintenance, and food loss), and communicate fully with professional refrigeration engineers.

Overview of Working Principles
1. Air Cooler
The air cooler forces air to flow over the evaporator coil through a fan, enabling heat exchange between the air and the refrigerant, thus achieving rapid cooling. It is typically used in scenarios requiring quick temperature reduction and high uniformity requirements.2. Gravity Coil
The coil relies on natural air convection, where the refrigerant evaporates inside the pipes, absorbing heat and cooling the surrounding air, which then sinks, creating an air circulation. Coils are typically installed at the top or on the walls of cold storage rooms and are suitable for environments sensitive to air velocity or requiring low temperatures with high humidity.Energy Efficiency Comparison
1. Cooling rate and temperature uniformity
Air cooler: Forced ventilation makes the distribution of cold air more uniform, with fast cooling speed, suitable for places with frequent entry and exit.Gravity Coil: The natural convection cooling rate is slow, but the temperature fluctuation is small, suitable for long-term storage and environments with high humidity requirements.
2. Energy consumption analysis
Air cooler: The fan motor consumes additional electrical energy, but is more efficient during high load operation. Modern air coolers typically use EC fans and intelligent speed regulation technology, which can save energy by 20% -30%.Gravity Coil: No fan consumes power, the system runs quietly, but in high temperature environments, the compressor load may increase due to low heat exchange efficiency.
3. Influence of humidity
Air cooler: Forced airflow can accelerate the evaporation of moisture on the surface of items, which may cause a decrease in humidity and is not suitable for storing humidity sensitive products such as fruits and vegetables.Gravity Coil: Natural convection is not easy to take away moisture, and the humidity inside the warehouse is well maintained, making it suitable for fresh-keeping storage.
Recommended Applicable Scenarios
Air coolers are more suitable for:
High temperature cold storage (above 0 ℃)Frequent inbound and outbound distribution centers
Places with high requirements for cooling speed
Scenarios with limited space requiring compact design
Gravity Coil is more suitable for:
Low temperature freezer (below -18 ℃)A fresh-keeping warehouse with high humidity requirements
Cold storage with long storage time and low frequency of inbound and outbound operations
Environment sensitive to noise
Long term operation and maintenance costs
1. Initial investment
Air cooler: The equipment cost is relatively low and the installation is relatively simple.Gravity Coil: requires a large amount of copper or aluminum pipes, with high material and installation costs.
2. Operation and maintenance
Air cooler: The fan motor needs regular maintenance, and the defrosting system may increase energy consumption.Gravity Coil: No moving parts, low failure rate, but long defrosting cycle and difficult pipeline cleaning.
3. Lifespan and reliability
Air cooler: The lifespan of the fan motor is usually 5-10 years, and the coil is prone to frost and needs to be treated regularly.Gravity Coil: The lifespan of the pipeline system can be over 15 years, with low maintenance requirements.
The direction of modern technological improvement
Air cooler: adopting high-efficiency EC fan, intelligent defrosting control, and variable frequency drive to further improve energy efficiency.Gravity Coil: Optimize pipeline layout and materials (such as aluminum pipes) to improve heat transfer efficiency and reduce filling volume.
Conclusion and Suggestions
There is no absolute 'best', only the most suitable solution. When making a choice, comprehensive consideration should be given to:Usage mode (temperature, turnover frequency of goods, number of door openings)
Energy prices
Initial budget and long-term operating costs
Food preservation requirements
General recommendation:
For dynamic environments such as logistics cold storage and supermarkets, air coolers are preferred to achieve fast response and uniform temperature.For low-temperature storage facilities located in areas with long-term frozen storage and high electricity prices, the long-term energy-saving benefits of pipeline drainage are more significant.
During the design and selection phase, conduct a full lifecycle cost analysis (including initial investment, electricity consumption, maintenance, and food loss), and communicate fully with professional refrigeration engineers.